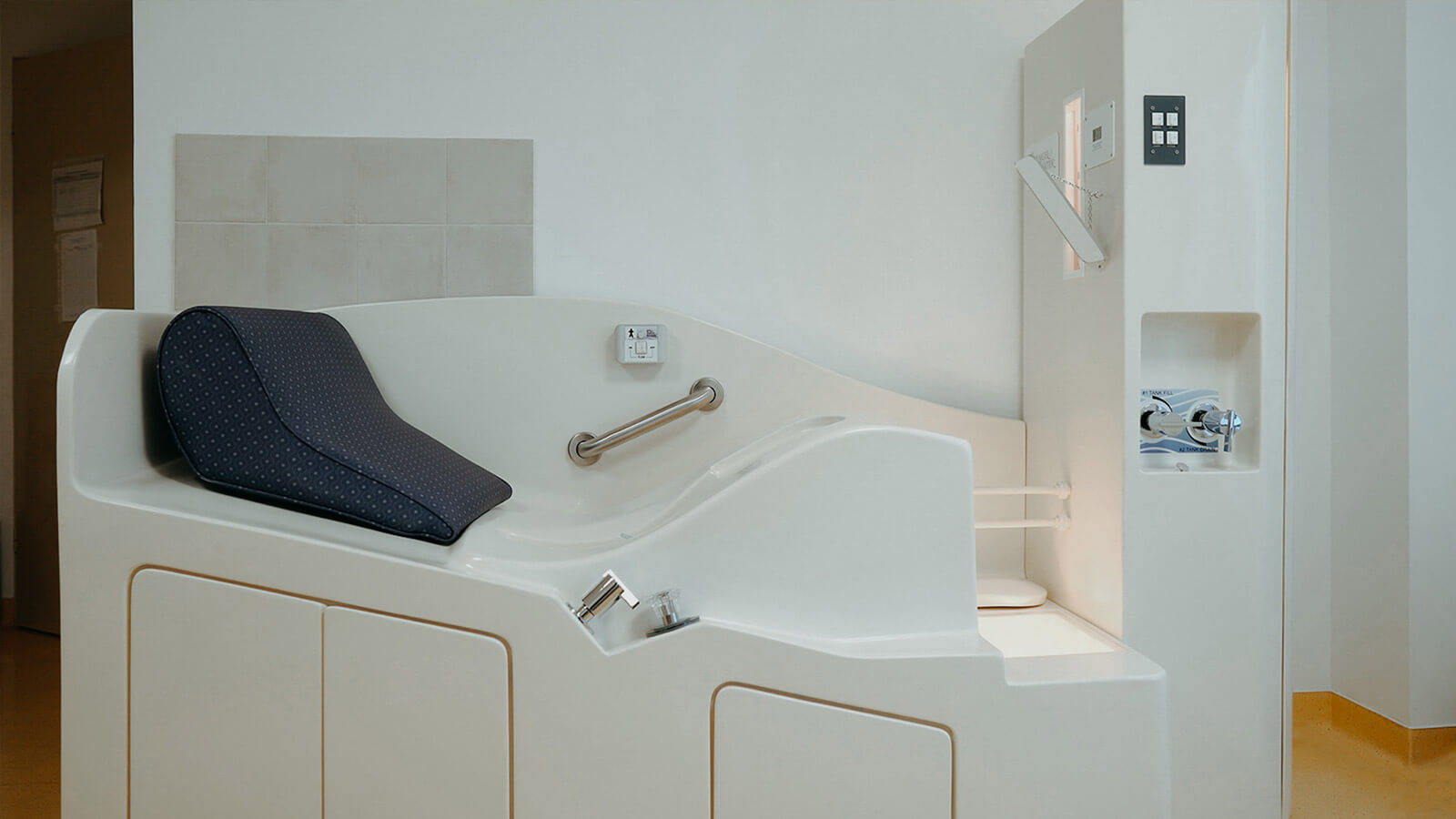
Intravenous laser in Lyme disease
Blue light
radiation
Lowers the level of inflammation in the body.
Stimulates complex I of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, increasing cellular ATP production.
Stimulating the production of reactive oxygen species destroys microorganisms in the bloodstream. The action is primarily evident in bacteria where blue light radiation produces reactive oxygen species through its absorption by bacterial porphyrins.
In combination with riboflavin, has antibacterial, antiviral, and antiparasitic effects.
Stimulates microcirculation by increasing NO.
Can be used as photosensitizers for antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (for bacterial, viral, and parasitic diseases) in combination with riboflavin and curcumin.

Red light
radiation
Stimulates immune function.
Activates macrophages.
Stimulates cytokine and interferon production.
Stimulates microcirculation and increases tissue oxygenation.
Stimulates cytochrome c activity, increasing ATP production in cells.
The therapeutic solutions we provide
Comprise a wide range of conventional, adjuvant and supportive therapies, which integrate medical concepts that have been built on a sturdy scientific basis and on the clinical experience of numerous Lyme disease specialists worldwide.
ImunoMedica patients have access to the latest diagnostic tools, technologies and innovations as well as to the latest and best treatments available, as soon as these are proven to be safe and effective.
How can you become a patient of our clinic?
Throughout the whole process, from your initial contact, through treatment and after you leave our clinic, our patient coordinators will guide you through the steps and support you with all their expertise, attention and kindness.
*
We are here to help you
Our patient coordinator will contact you soon
Phone: +40.771.518.946, e-mail: office@imuno-medica.ro