Cancer Treatment at the ImunoMedica Clinic
Our clinic's main goals in the fight against cancer are to optimize the body's own defense mechanism by improving its immune response, to enhance the antitumoral effect of conventional therapies, and to mitigate their side effects.
We also address the multidrug resistance mechanisms that are usually the reason behind cancerous metastases. This way, we achieve a better response to conventional therapies and increase the immune system's efficacy in targeting cancerous cells and tumors.
Innovative approaches
The therapeutic solutions we provide comprise a wide range of conventional, adjuvant and supportive therapies, which integrate medical concepts that have been built on a sturdy scientific basis and on the clinical experience of numerous cancer specialists worldwide.
ImunoMedica patients have access to the latest diagnostic tools, technologies and innovations as well as to the latest and best treatments available, as soon as these are proven to be safe and effective. It is only by continually striving to overcome the limits of the medical act which has turned conventional, that we are able to offer our patients the best chance to regain their health, of that we are certain.

Conventional
therapies
A key focus of our therapeutic approach is on strategies for enhancing the antitumoral effects of chemotherapy, while minimizing its side effects. Moreover, chemotherapy is considered in the context of a multimodal approach, and it is supported by immunotherapies and molecularly targeted therapies.

Molecularly
targeted therapies
The core of precision medicine lies in tailoring a personalized therapeutic strategy based on the patients' genotype and targeted therapies. This way, the chosen therapeutic scheme will be one in which the monoclonal antibodies from immunotherapies are combined with other targeted therapeutic agents to maximize cytotoxicity while minimizing side effects. The molecularly targeted therapy allows for a very precise and efficient administration of the medicine, as it only targets the tumor cell. Thus, the toxicity is much lower compared to conventional chemotherapy.
Adjuvant therapies
It is becoming increasingly difficult to draw a line between conventional adjuvant therapies and their newest counterparts, which have very good results with tumor regression in the healing process and help increase the patient's survival rate. In the scientific literature, therapies such as hyperthermia, administration of herbal extracts such as curcumin, and oxidative therapies are increasingly being included in the category of adjuvant cancer therapies.
According to research, the best way to avoid treatment resistance is to combine therapies that synergistically block as many resistance mechanisms action pathways as possible. As a result, in our clinic, the multimodal approach in adjuvant therapies is demonstrating its efficacy by lowering the rate of treatment adverse effects and achieving therapeutic success.
Angiogenesis
Since angiogenesis plays a critical role in tumor growth and metastasis, we pay special attention to antiangiogenic therapies. In addition to conventional antiangiogenic therapies based on drugs like Bevacizumab, several natural compounds, including EGCG and polyphenols, have been found to have a strong antiangiogenic effect.
The Metabolic
approach
Tumor cells, in general, metabolize glucose, lactate, pyruvate, hydroxybutyrate, acetate, glutamine, and fatty acids at significantly higher rates than normal cells. In this context, metabolic therapy uses those drugs and supplements that block the metabolic pathways that cancer cells use to receive nutrients and produce energy. The tumor cell becomes much more sensitive to antitumoral therapies as a result.
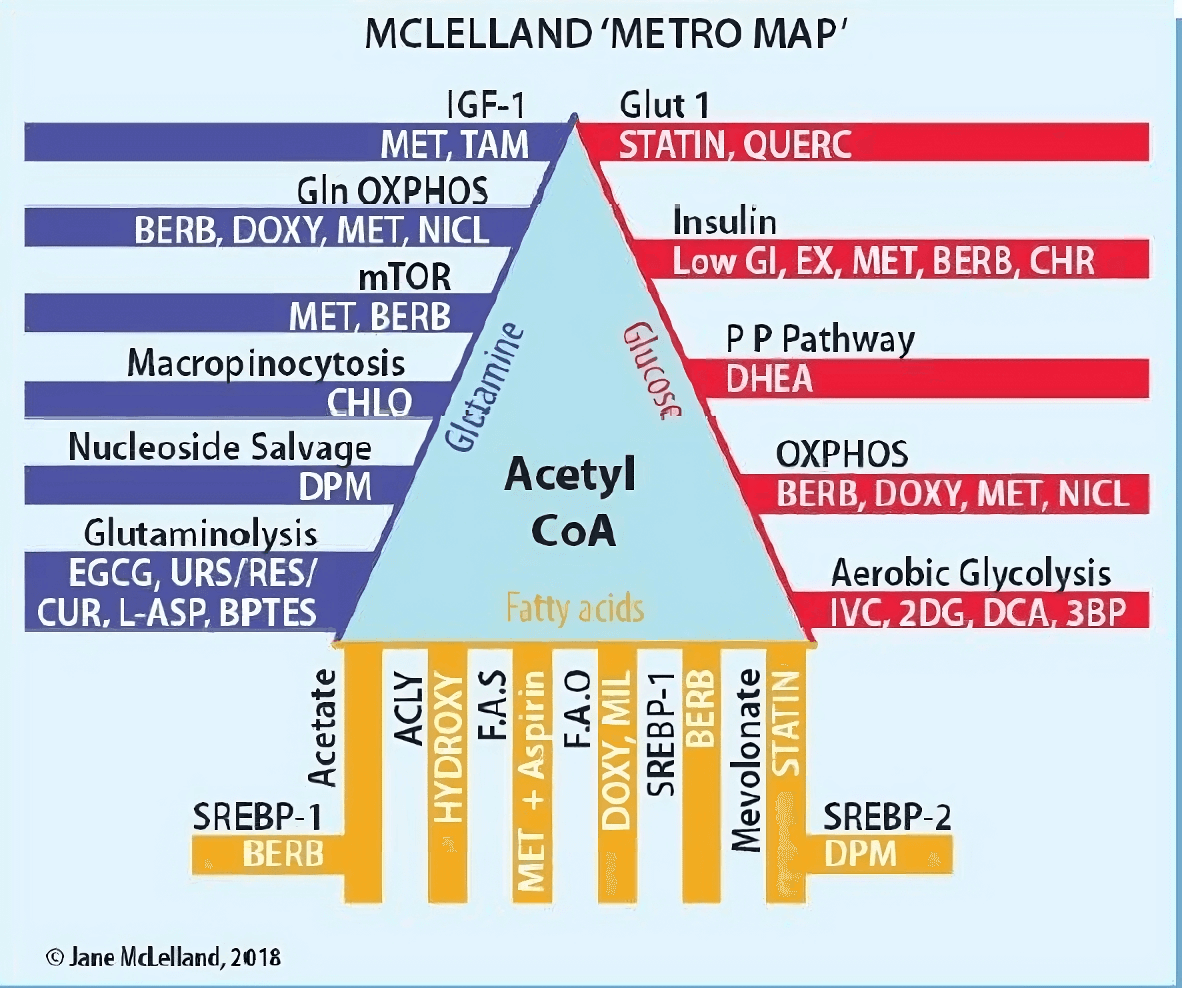
McLelland metro map from the book How to Starve Cancer author Jane McLelland, used with the author's permission.
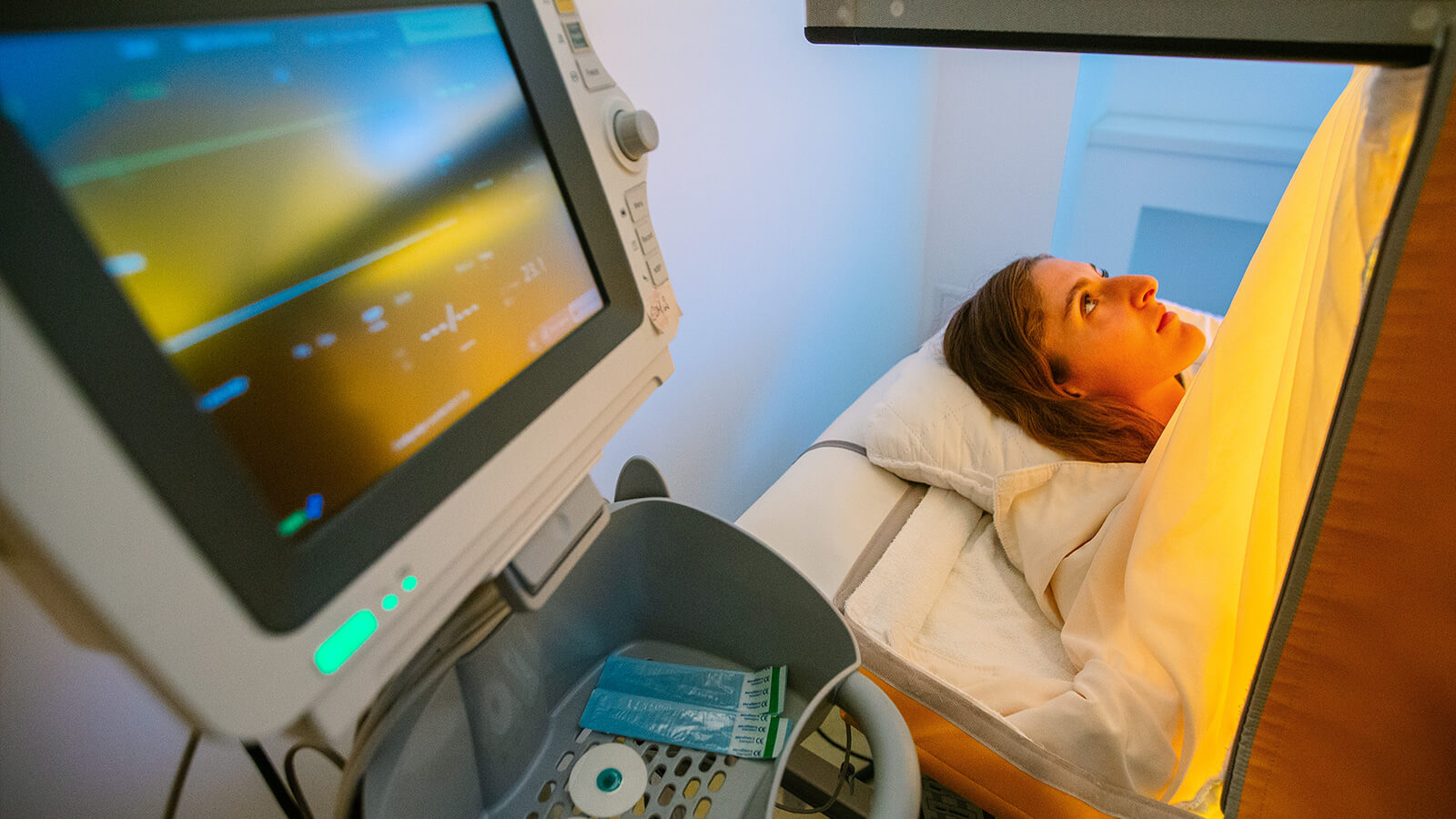
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is considered one of the most important adjuvant therapies in cancer treatment. Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and other cytostatic therapies work better when blood flow to the tumors is improved, which occurs when the tumor temperature is raised to about 44 °C through local hyperthermia. The overheating of these tumors also results in the release of 'heat shock proteins,' which signal the immune system to identify and eliminate cancer cells. Another important phenomenon is the enhancement of the immune response caused as a result of an increase in body temperature above 39.5 °C in whole-body hyperthermia.
Anti-inflammatory
therapies
Numerous clinical trials have shown that inflammation plays a key role in the initiation, progression, and prognosis of cancer. This explains why anti-inflammatory therapies have the potential to improve the efficacy of conventional therapies, while also acting as a monotherapy treatment for many solid tumors. Anti-inflammatory therapies have also proven effective not only in halting tumor progression, but also in boosting immunity, when used in conjunction with various immunotherapies, making them an important component of cancer treatment.

Multimodal
immunotherapies
Immunotherapies, in addition to standard therapies, play an essential role in cancer treatment today. Cancer itself is evidence of a failure of the immune response to control its formation, development and progression, so the aim of immunotherapies is none other than to amplify the immune response and target it towards the destruction of tumor cells. Immunotherapies are currently available in a variety of forms, but all aim to activate the immune response via NK, NKT, and T cells using various strategies. A positive prognosis can be given when, regardless of the immunotherapy used, immune cells are successful in their fight against tumor cells.

Oxidative
therapies
The production of more reactive oxygen species (ROS) is one of the most effective anti-cancer therapy strategies because it can accelerate antitumoral signalling and, through oxidative stress, trigger tumor cell apoptosis and immunological modulation toward tumor regression. While conventional therapies increase oxidative stress throughout the body, causing apoptosis or genetic defects in normal cells, certain natural compounds or oxidative therapies are useful in that they can direct oxidative stress exclusively at tumor cells, protecting thus the cells in healthy tissues.
Natural anticancer compounds
that are perfusable
According to scientific evidence, many natural compounds directly or indirectly target multiple signalling pathways and networks in cancer cells, resulting in a significant antitumoral effect. Thus, combining conventional therapies with the administration of polypharmacological extracts derived from plants or compounds may provide a significant advantage in sensitizing monotherapy efficacy and overcoming drug-induced resistance in cancer patients. The major effects, however, occur when these compounds are administered parenterally, as their oral absorption is typically extremely poor.
Supportive therapies
Anti-cancer therapies, which primarily target tumor cells, do not address the psychosomatic conditions that led to cancer. Furthermore, the disease itself deepens those procarcinogenic mechanisms by providing new opportunities for proliferative mechanisms to manifest.
The body's capacity to fight the illness will be diminished as a result, and the likelihood of recovery and relapse will both be enhanced. Supportive therapies not only aid in healing by assisting the body in coping with the illness and treatment, but they also reduce or completely eliminate the chance of cancer recurring in any way.
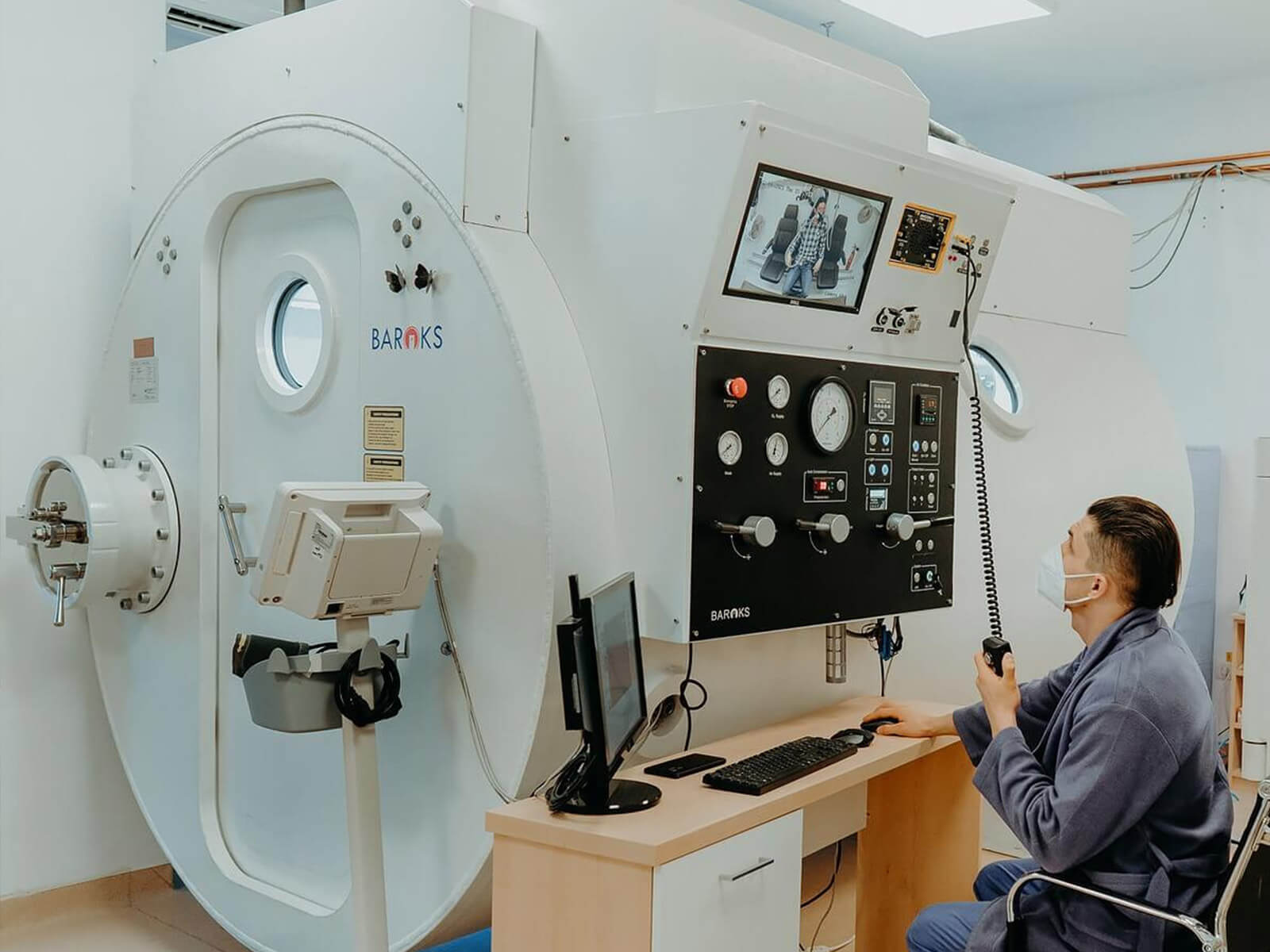
Therapies that increase
oxygenation
Hypoxia is one of the most important factors in tumor cell survival, resulting in a highly aggressive tumor phenotype. The effects of hypoxia include increased angiogenesis, increased glycolytic metabolism, decreased tumor cell apoptosis potential, and enhanced proliferative and metastatic potential. Hypoxia also decreases the sensitivity of tumors to radiotherapy and various chemotherapies. These are just a few of the reasons why cell oxygenation-enhancing therapies are so important in cancer treatment.

Nutrition
In terms of both the metabolic strategy and the clinical changes that occur in cancer, nutrition plays a critical role in the treatment of the disease. The choice of dietary intervention must take into account the effectiveness of the therapy, the minimization of side effects and problems, the improvement of quality of life, and the survival rate. Depending on the type of cancer and its metabolism, the patient's health, and the cancer therapies the diet is included in, one may choose an alkaline, ketogenic, low-carb, or high-fat diet. Although there are a few nutrients that are crucial in cancer, we don't believe in standard anti-cancer treatments.
Modulation of
the bile acid - gut microbiome axis
Recent studies have shown that the occurrence of some types of cancer is related to the nature of the microbiome, specifically to the way it regulates certain metabolic and immune processes. It has recently been discovered that the microbiome-biliary acid axis plays a major role in the carcinogenic or immunoprotective process. This is due to the fact that bile acids have the ability to taxonomically modulate the microbiome, which in turn can signal the production of a specific quantity and composition of bile acids. Thus, studies have demonstrated that a certain type of microbiome may either generate or inhibit cell proliferation, inflammation, and cancer, both directly and through the bile acids metabolized inside it. As a result, the success of cancer therapy may be heavily reliant on microbiome and bile acid health.
Detoxification
therapies
Heavy metals and xenobiotics are both major factors in the development of cancer. The toxicity of conventional anti-cancer therapies can also lead to increased intoxication of the body, potentially worsening the patient's situation. These are only a few of the factors that make detoxification therapies so important in the treatment of cancer.
Manual therapies
Manual therapy have been shown to improve the quality of life of cancer patients over time. It has been demonstrated that these therapies can alleviate particular cancer-related symptoms such as pain, nausea, vomiting, extreme fatigue, breathing difficulties, anxiety, lymphoedema etc. Such treatments frequently assist the patient in overcoming circumstances that threaten not only his health but also his confidence in the course of treatment, and they generate a particular psychological state that favours a positive prognostic for the therapies being used.

New technologies
Technology is continuously revealing new possibilities in the treatment of numerous diseases, including cancer. Some of these therapies have a straight antitumoral effect. Others lessen treatment side effects or provide an environment that is favourable for conventional and adjuvant therapies. When they are all combined, however, they lay the groundwork for a complex strategy that maximizes or optimizes the benefits of therapy, leading to treatment success and a favourable future prognosis.

Psychological life
and spirituality
Given that the soul and the body are inextricably linked, anything that promotes mental and emotional peace, calm, and an escape from conflict states, is essential for the therapy to progress in a healthy way. This reality makes spirituality or religious life, as well as psychotherapy, essential prerequisites for well-being, for achieving a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, and reaching a higher quality of life.
Physical and breathing exercises
When cancer develops as a result of a lifestyle that is largely sedentary, exercise can help with cancer treatment. Studies have shown that physical exercise, particularly anaerobic activity, is crucial for a number of physiological functions such as: improving insulin sensitivity and suppressing glycolysis, lowering fatigue, boosting the immune system, preventing cachexia and, most importantly, improving the quality of life. Anaerobic exercise has also been shown to improve the apoptotic processes in cancer cells, which has been linked to a reduction in tumor mass.
Frequently asked
questions about
cancer treatment
in the ImunoMedica Clinic:
-
How long does cancer treatment last in Clinica ImunoMedica?
The length of treatment depends on the type of cancer, its stage, the patient's condition, and, of course, the latest test results.
-
What are the side effects of the proposed therapies?
Specific toxicity implies any treatment with drugs, especially cytostatics. In our clinic, however, we pay particular attention to therapeutic strategies that minimize the adverse effects of toxic therapies. One of these is the intravenous administration of natural extracts that are synergistic with cytostatics or immunotherapies and reduce their negative effects.
-
Which therapies are more effective in treating cancer: oxidative or antioxidant therapies?
Oxidative therapies are generally used in chemotherapy to destroy tumor cells. Thus, we could say that oxidative therapies prove more effective in the fight against cancer. However, there are natural compounds, such as vitamin C and Curcumin, which in high doses have strong oxidative effects, although, in small amounts, they are antioxidants. Other natural compounds, such as Artesunate, regardless of the portion used, have a substantial oxidative effect. All these and many other natural oxidative therapies are also used in our clinic to fight cancer. They also play a positive role in oncological treatment, especially in protecting the body against oxidative stress, but also in the detoxification processes that are so important in this disease.
-
Don't antioxidant therapies cancel out the effect of oxidative therapies?
In our clinic, we do not simultaneously administer oxidative and antioxidant therapies, but the antioxidant treatments after oxidative therapies have taken effect. There are other mechanisms of anti-cancer action, such as those that increase the pH around tumors to make them more vulnerable. Some therapies block their feeding pathways, immune or targeted therapies, which do not fit into the oxidant-antioxidant logic, and can be coupled with any of the treatments that raise the immune response, whether they are oxidative, such as ozone therapy or antioxidant.
-
Can therapy lead to a worsening of symptoms?
In most cases, the therapies are accompanied by a rapid improvement in quality of life, reflected in reduced pain, if any, and improved sleep quality and mood. However, there are also cases where, temporarily, the pain intensifies following tumor lysis or tumor response to treatments, especially in the tumor area. This reaction is only a sign of the effectiveness of the therapy, and the pain is only temporary and occurs mainly during the therapeutic procedure.
-
Can I receive a personalized treatment plan?
In our clinic, we pay special attention to personalized therapies. The patient coordinators in our clinic will find the most appropriate solution for each one. Of course, we need more information about your health condition, disease history, and tests to offer you a preliminary treatment plan in our clinic.
How can you become a patient of our clinic?
Throughout the whole process, from your initial contact, through treatment and after you leave our clinic, our patient coordinators will guide you through the steps and support you with all their expertise, attention and kindness.
*
We are here to help you
Our patient coordinator will contact you soon
Phone: +40.771.518.946, e-mail: office@imuno-medica.ro